In the era of cloud computing and rapid software deployment, a log monitoring system is indispensable for maintaining system reliability, security, and performance. But what is log monitoring? It’s the real-time tracking of log data—event records from systems, applications, or networks—to detect issues, anomalies, or security threats instantly. This blog explores how to build an effective log monitoring system, highlights top log management tools and log monitoring tools (including open-source options), and explains how it differs from log analysis. We’ll also cover why logging and monitoring are important in a cloud environment, especially for frontend teams, and evaluate the best logging solutions for cloud frontend and cloud logging platforms.
Monitoring systems typically monitor system log files and other logging data for issues and incidents (performance, error, and security) via real-time detection. Such systems do not perform log analysis to gain insights from historical data; they detect and alert on the immediate, the now. An example of monitoring is during application log monitoring (see CI and CD below) spike in API errors, or during security logging and monitoring an alert could indicate unauthorized access attempts by an external party, so that you could respond right away.
What are system log files? These are event records generated by operating systems, applications, or devices, including information such as timestamps, error codes, or actions performed by users. Log monitoring systems utilize device log analyzers to flatten the logs into a single view of system health.
Logging and monitoring are critical in cloud environments due to their distributed and dynamic nature. Cloud systems generate massive amounts of log data across services, making a robust log monitoring system essential for tracking issues. Logs from user-facing applications (e.g., web servers or APIs) are essential for frontend teams to detect latency or UI errors. Why is logging and monitoring important in a cloud environment? By logging and monitoring, you maintain maximum uptime for your applications, enhance user experience, and enhance security through real-time detection of threats (i.e. DDoS, breaches). A well-designed log monitoring system can help as it relates to regulatory obligations such as GDPR or HIPAA through audit trails.
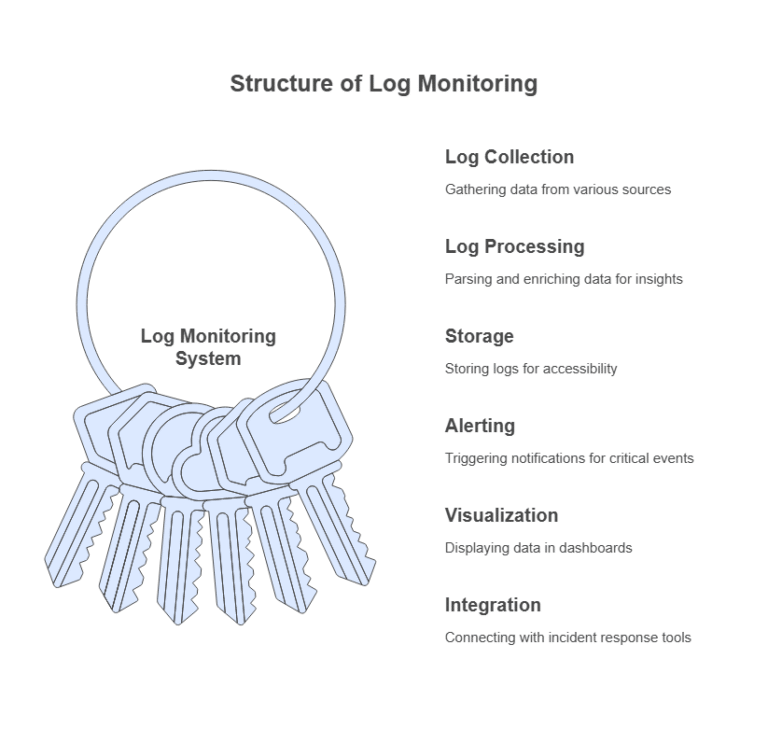
A log monitoring system comprises several components:
Several log monitoring tools and top log management tools enable a scalable log monitoring system. Here are some of the best, including open-source log monitoring tools option:
Front end teams want a cloud logging platform that is easy to use, provides real-time insight, and has cloud native support. Grafana Loki and Kibana are among the best logging solutions for cloud frontend because of their lightweight architecture and good visualization. For instance, Grafana works with AWS or Azure giving front-end teams the means of tracking API response time or client side errors. Elasticsearch with Kibana is also one of the top contenders, particularly good querying and dashboards. It’s great for application logging in cloud environments.

Key techniques for an effective log monitoring system include:
A log monitoring system and log analysis both handle log data but serve different purposes:
For example, a log monitoring system might alert frontend teams to a spike in 500 errors, enabling quick action. Later, log analysis could reveal a database bottleneck causing those errors, suggesting infrastructure improvements.
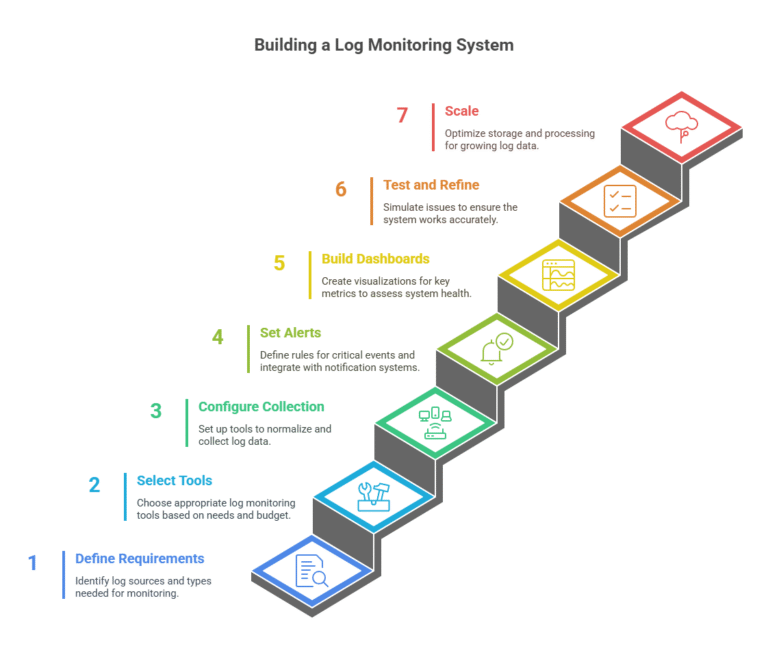
Log monitoring systems are an essential component of cloud contract initiatives to help maintain reliable, secure, and performant systems. By using the best log management tools and processors like Fluentd, Elasticsearch, and Grafana and methods like real-time parsing, and anomaly detection on the logs, we can build powerful systems. Why are logging and monitoring so important to cloud environments? Logging provides system uptime, security enhancement, and compliance.
For front-end teams, the leading cloud logging platforms, such as Grafana Loki or Kibana, focus on application log monitoring. Solutions like DevSecCops.ai, which is an AI DevOps platform, further add value to a log monitoring system by leveraging security scanning solutions integrated with DevOps capabilities. This integration automates threat detection and compliance checks so that the front-end team can take quicker action and have a clearer operational workflow. Log monitoring systems allow teams to take action in real-time but are intended for log monitoring even more in the long run, ensuring operational efficiency and longer-term growth.